Delving Into The Stats: Unemployed Worldwide Continues To Spike
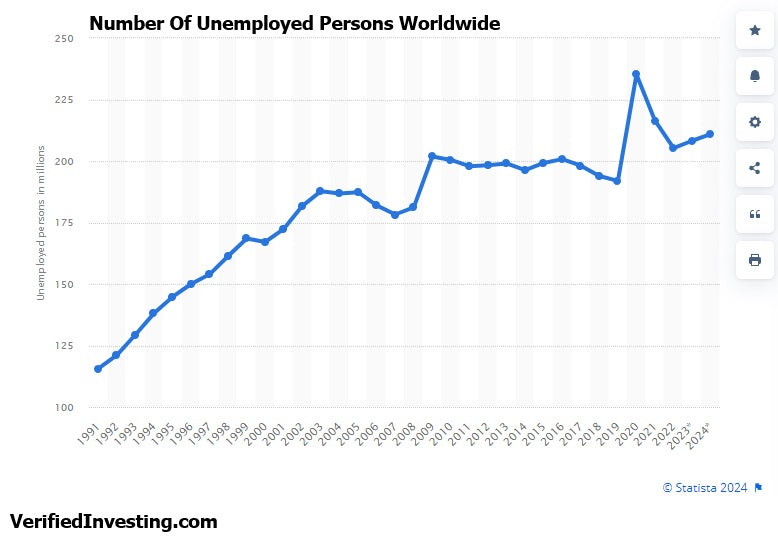
As good as the world appears to be doing by the headlines in the media, unemployment worldwide continues to rise. This can be seen in the chart above, up nearly 100% since 1991 from 115 million to 210 million.
This paints a picture of a global economy where a large percentage of people are struggling, as the wealth disparity continues to grow. Below let's delve into the reasons.
1. Technological Advancements and Automation:
- Job Displacement: Automation and technological advancements, while increasing productivity, have also led to job displacement in various sectors, particularly manufacturing and routine tasks. Workers lacking the skills to adapt to these changes find themselves unemployed.
2. Globalization and Shifting Labor Markets:
- Outsourcing: Companies often relocate manufacturing and other jobs to countries with lower labor costs, leading to job losses in developed economies.
- Increased Competition: Globalization has intensified competition, forcing companies to streamline operations and reduce their workforce to remain competitive.
3. Demographic Changes:
- Aging Population: In many developed countries, an aging population and declining birth rates contribute to a shrinking workforce and slower economic growth.
- Youth Unemployment: In some regions, a large youth population struggles to find employment due to a lack of skills or suitable job opportunities.
4. Economic Shocks and Crises:
- Financial Crises: The 2008 financial crisis and other economic downturns have led to significant job losses and slow recoveries.
- Global Pandemic: The COVID-19 pandemic caused widespread disruptions to businesses and labor markets, resulting in a sharp increase in unemployment.
- Geopolitical Instability: Conflicts and political instability can disrupt supply chains, reduce investment, and lead to job losses.
5. Inequality and Wage Stagnation:
- Unequal Distribution of Wealth: Rising income inequality means that the benefits of economic growth are not shared equally, leaving many workers with stagnant wages and limited opportunities.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Wage stagnation can dampen consumer spending, which in turn affects business growth and employment opportunities.
6. Skills Gap:
- Mismatch between Skills and Jobs: A growing mismatch between the skills workers possess and the skills employers demand contributes to unemployment. This highlights the need for education and training programs to address this gap.
Consequences of Rising Unemployment:
- Reduced Economic Growth: High unemployment leads to lower consumer spending and reduced economic activity.
- Social Unrest: Unemployment can contribute to social unrest, poverty, and increased crime rates.
- Mental Health Issues: Job loss can have a significant impact on mental health and well-being.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including investments in education and skills training, policies that promote inclusive economic growth, and international cooperation to manage global economic risks.
Trading involves substantial risk. All content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice or recommendations to buy or sell any asset. Read full terms of service.




