Federal Reserve's Balance Sheet: Positives And Negatives
Published At: Mar 02, 2025 by
Gareth Soloway
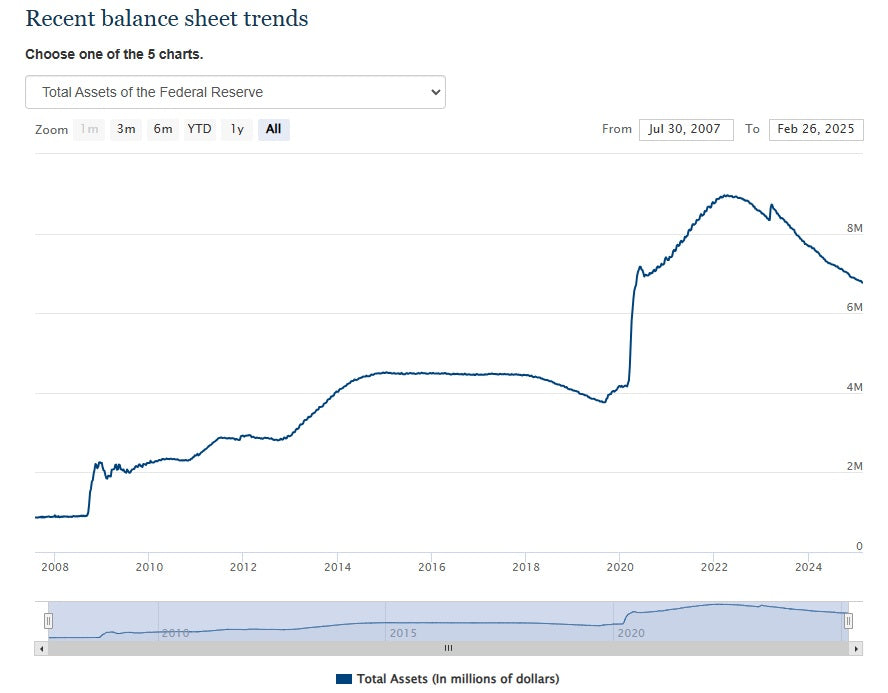
The Federal Reserve's balance sheet is a critical tool in the U.S. central bank's arsenal, reflecting its assets and liabilities. It plays a pivotal role in implementing monetary policy and maintaining financial stability. Here's a breakdown of its key aspects:
What is the Federal Reserve's Balance Sheet?
- Essentially, it's a financial statement that outlines the Fed's assets (what it owns) and liabilities (what it owes).
- Assets primarily consist of U.S. Treasury securities and mortgage-backed securities (MBS).
- Liabilities include currency in circulation and reserves held by commercial banks.
How it Works
- The Fed uses its balance sheet to influence the money supply and interest rates.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): During economic downturns, the Fed may expand its balance sheet by purchasing assets, injecting money into the economy and lowering interest rates.
- Quantitative Tightening (QT): Conversely, to combat inflation, the Fed may shrink its balance sheet by selling assets or allowing them to mature, which removes money from circulation and raises interest rates.
Positives of a Large Federal Reserve Balance Sheet
- Supporting Economic Growth: In times of crisis, a large balance sheet can provide much-needed stimulus, helping to prevent a deep recession.
- Stabilizing Financial Markets: The Fed's asset purchases can help to stabilize markets during periods of stress, preventing disruptions to the flow of credit.
- Lowering Interest Rates: By purchasing assets, the Fed can drive down interest rates, making it cheaper for businesses and consumers to borrow money.
Negatives of a Large Federal Reserve Balance Sheet
- Inflation Risk: Injecting large amounts of money into the economy can lead to inflation if not carefully managed.
- Asset Bubbles: Prolonged periods of low interest rates can create asset bubbles, where asset prices become inflated beyond their fundamental value.
- Financial Instability: An excessively large balance sheet can make it more difficult for the Fed to respond to future economic shocks.
- Distorting market signals: when the Federal reserve buys large quantities of assets, this distorts the natural forces of supply and demand that would otherwise create a market based price for those assets. This can lead to miss-allocation of resources.
Trading involves substantial risk. All content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice or recommendations to buy or sell any asset. Read full terms of service.




