Credit Card Delinquency Rates Spike To Highest Since Great Recession
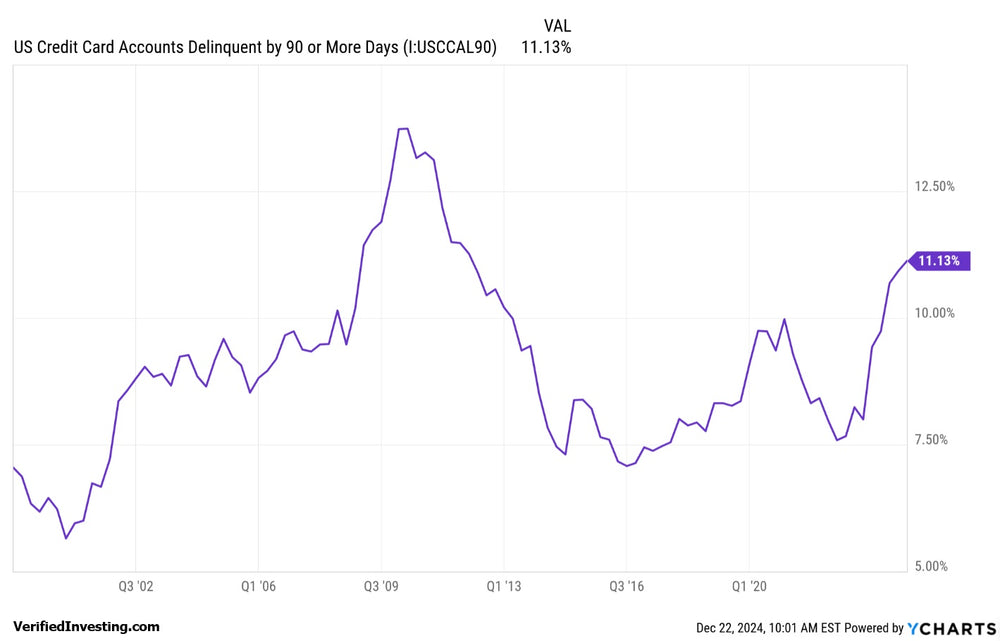
Credit card delinquencies have spiked to 11.13%. These are credit card payments that are late at least 90 days. This is the highest number since the Great Recession in 2009 and the spike in delinquency rates is also being seen in other areas. Let's take a deep dive.
The recent surge in delinquency rates across various debt categories is a concerning trend that reflects several underlying economic factors. As an economist, I see this as a potential signal of broader economic challenges that warrant close attention. Here's a breakdown of the key factors contributing to this phenomenon:
1. Inflation and Eroding Purchasing Power:
The persistent inflationary pressure we've experienced has squeezed household budgets. The rising cost of essential goods and services leaves less disposable income for debt repayment, pushing more individuals towards delinquency.
2. Rising Interest Rates:
The Federal Reserve's response to inflation has involved a series of interest rate hikes. This translates to higher borrowing costs, making it more expensive to service existing debt like credit cards and mortgages. Consequently, some borrowers struggle to meet their obligations, leading to an uptick in delinquencies.
3. Economic Slowdown and Job Losses:
Economic growth has slowed in recent months, and there have been job losses in certain sectors. Unemployment or reduced income directly impacts an individual's ability to manage debt, contributing to the rising delinquency rates.
4. Overextension of Credit:
The easy availability of credit in previous years may have encouraged some borrowers to take on more debt than they could comfortably handle. As economic conditions tighten, these borrowers are now facing difficulties in managing their debt burden.
5. Pandemic-Related Support Measures Ending:
Government support programs implemented during the pandemic, such as loan forbearance and stimulus checks, have largely ended. This sudden withdrawal of support has left some borrowers vulnerable, contributing to the increase in delinquencies.
Why It Matters:
Rising delinquency rates have significant economic implications:
- Increased Financial Stress on Households: Delinquencies lead to late fees, penalties, and potential damage to credit scores, further straining household finances.
- Losses for Lenders: Lenders face potential losses when borrowers default on their loans. This can impact their profitability and lending practices.
- Potential for Broader Economic Impact: A significant increase in delinquencies can signal a weakening economy and potentially lead to a credit crunch, further hindering economic growth.
Trading involves substantial risk. All content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice or recommendations to buy or sell any asset. Read full terms of service.