The U.S Debt-To-GDP And Its Economic Implications
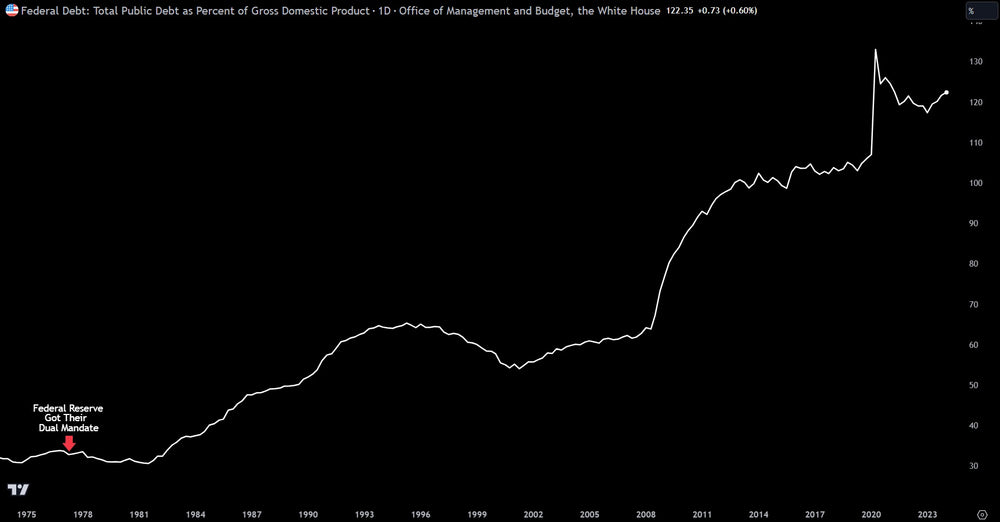
The U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio is a crucial economic indicator that compares the country's total national debt to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
It essentially shows how much the government owes compared to the total value of goods and services produced within the country in a year.
Key Points:
-
Current Situation: As of 2023, the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio is approximately 122.3%, which means the national debt is larger than the entire annual economic output of the country.
-
Historical Context: This ratio has been rising in recent years, especially after the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic. Historically, the U.S. has seen much lower ratios, with an average of 65.7% from 1940 to 2023.
-
Implications: A high debt-to-GDP ratio can have several implications:
-
It may raise concerns about the government's ability to repay its debts, potentially leading to higher borrowing costs.
-
It can limit the government's fiscal flexibility to respond to future economic downturns or other crises.
-
It might crowd out private investment, as the government competes with businesses for available funds.
-
It may raise concerns about the government's ability to repay its debts, potentially leading to higher borrowing costs.
Nuances:
- While a high debt-to-GDP ratio is a cause for concern, it's important to consider other factors like interest rates, economic growth prospects, and the composition of the debt.
-
The U.S. dollar's status as a global reserve currency allows the U.S. to borrow at relatively low interest rates, even with a high debt level.
-
There is ongoing debate among economists about the "sustainable" level of debt-to-GDP ratio and its long-term impact on the economy.
In conclusion: The U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio is a significant economic indicator that warrants close monitoring. While the current high ratio raises concerns, its implications depend on various other factors, and the long-term consequences remain a subject of ongoing debate.
Trading involves substantial risk. All content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice or recommendations to buy or sell any asset. Read full terms of service.