Understanding M2 Money Supply And How It Has Changed
Published At: Jul 21, 2024 by
Gareth Soloway
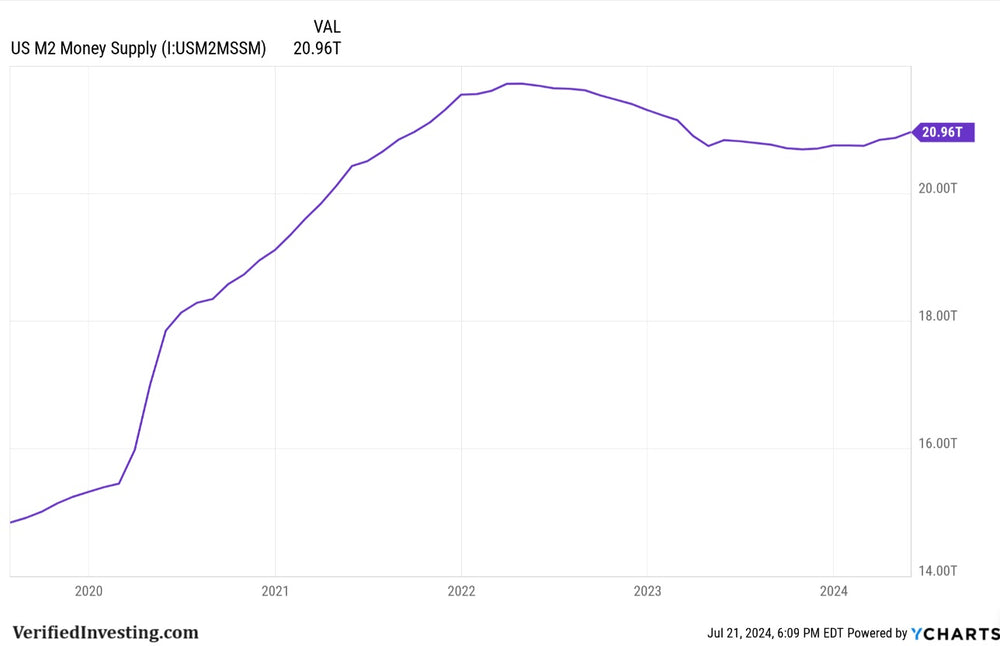
M2 is a measure of the money supply that includes cash, checking deposits, and easily convertible near money.
Components of M2:
- M1: This includes physical currency (coins and paper money) and demand deposits (checking accounts).
- Savings deposits: This includes money held in savings accounts.
- Small-denomination time deposits: These are certificates of deposit (CDs) under $100,000.
- Retail money market funds: These are funds that invest in short-term debt securities.
Why M2 is Important:
- Economic Indicator: The M2 money supply is a key economic indicator. It is closely watched by economists and policymakers to assess the health of the economy and potential inflationary pressures. Rapid growth in M2 can be a warning sign of inflation, while slow growth might suggest a weakening economy.
- Monetary Policy: The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, uses M2 as one of several guides when setting monetary policy. It may adjust interest rates or engage in open market operations to influence the growth of M2 to achieve its goals of price stability and maximum employment.
M2 money supply has surged since Covid in 2020. However, once the Federal Reserve began hiking interest rates it did start to shrink. However, like with many things to do with the Federal Reserve, it shrinks slightly, expands massively, then shrinks slightly before massively expanding again.
Generally, the more M2 in the system, the higher the inflation.
Trading involves substantial risk. All content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice or recommendations to buy or sell any asset. Read full terms of service.